1) Filled-Volume Calculator
2) Turnover Target & Species Factor
3) Head-Loss & Plumbing Estimator
4) Real-Flow Reality Check
5) Bio‑Media Surface Area Planner
6) Redundancy vs One‑Big Filter
Monthly energy: —
7) Energy Cost Calculator
8) Canister Selector Table
| Brand/Model | Rated Flow | Estimated Flow | Max Head | Canister Volume (L) | Baskets | Hose ID | Watts | Typical Price | Notes |
|---|
9) Flow Pattern & Placement
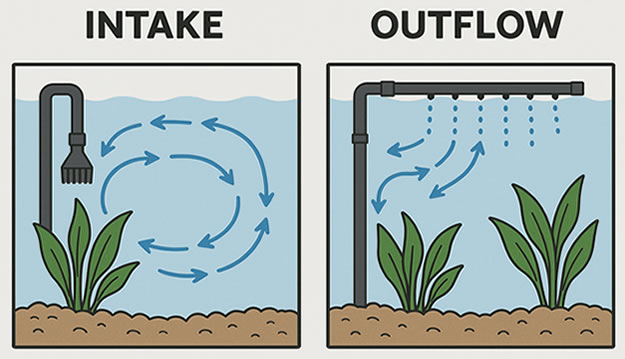
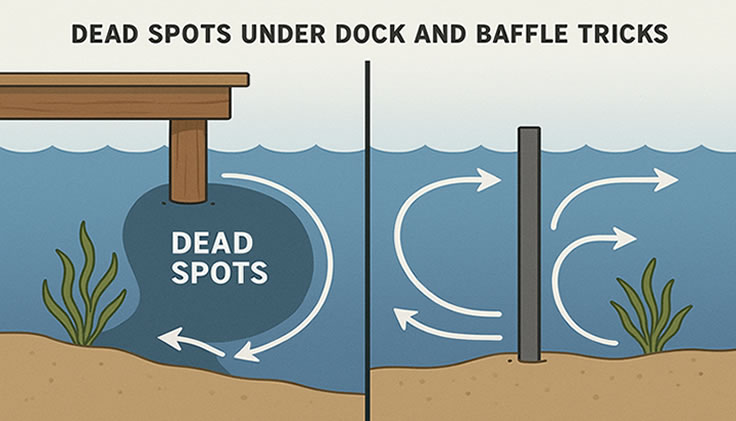
Aim the spray bar along the long side to create a gentle gyre, keep intake low on the opposite end, and avoid blasting the basking spot. If turtles struggle against current, angle the bar toward the glass and slit the far end for pressure relief.
10) Maintenance Planner
11) Water Quality Targets & Testing
Keep Ammonia: 0, Nitrite: 0, and Nitrate: < 40 ppm for turtles. Test weekly until stable, then at least biweekly. If nitrate trends up, increase water changes, reduce feed, and evaluate media clogging.
12) Safety, Noise & Reliability
- Use an intake guard for hatchlings, add a drip loop, and prime carefully after service.
- Seat baskets firmly to prevent bypass; purge air to stop microbubbles and rattling.
- Place the canister on a soft pad, keep hose runs smooth and wide radius to reduce vibration and head loss.
- Have a power‑outage plan: a small battery air pump can prevent crashes.
13) Troubleshooting Matrix
| Symptom | Likely cause | Quick fix |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudy water after cleaning | Bypass or disturbed bio-film | Re-seat baskets, run with polishing pad for 24h |
| Flow drops over days | Clogging in prefilter or impeller | Rinse coarse sponge weekly, inspect impeller well |
| Rattling/cavitation | Air trapped, spray bar too restrictive | Tip the canister to purge, slit spray bar end |
| Microbubbles | Leaky intake or outgassing | Check hose clamps, warm water to degas |
| Ammonia spike | Overcleaned media or dead spots | Stagger media cleaning, adjust flow pattern |
14) Worked Examples
Example A: 75‑gallon RES juvenile
At 36×18×20″ with 16″ water height and 5% décor, filled volume ≈ 72 gal. Target turnover 8–10× → 576–720 GPH. With 2 ft lift, 8 ft round-trip of 1/2″ hose, two elbows, and typical media, η_head ≈ 0.78, η_media ≈ 0.72. Cleaning every 21 days gives η_clog ≈ 0.73; with prefilter bonus 1.05. A canister rated ~1000 GPH would yield Q_real ≈ 1000×0.78×0.72×0.73×1.05 ≈ 430 GPH → short. Two mediums rated 550 GPH each in parallel estimate ≈ 2× (550×0.78×0.72×0.73×1.05) ≈ 474 GPH: still borderline; raise turnover or shorten head and clean more often.
Example B: 40‑breeder musk/mud
Lower bio-load allows turnover 6–8×. With shallow 12″ water height and wide footprint, prioritize gentle gyre and large prefilter. A 400–500 GPH rated unit may suffice depending on plumbing.
Example C: High décor with spray bar and 1.2 m lift
Spray bars add backpressure; ensure holes are large and tip is open. Widen hose ID where possible to regain η_head.
15) FAQ
16) Downloads & Printables
Export your summary and table as CSV, print this page as a PDF, or grab calendar reminders.